What Is Chickenpox? Why Do You Only Have Once In Your Life?
At the word chickenpox, almost no one can be indifferent. It is one of the most contagious diseases known and, in general, people tend to associate it with childhood. However, it can also be suffered in other stages.
In children, chickenpox is rarely serious. Now, in adults with T-cell immunodeficiency and in patients receiving chemotherapy or corticosteroid medication, there are increased risks.
Let’s see more about it.
Chickenpox, a well-known infection
Chickenpox is acquired from inhaling airborne droplets expelled by someone infected with the varicella virus (varicella-zoster virus: VVZ). We clarify that chickenpox is contagious two days before the rash appears.
It has a latency process of two to three weeks, that is, this time elapses from contagion to the development of the disease. During this time, a series of events take place. First, the virus lodges in the upper respiratory tract (throat, roughly). It then reproduces in the regional lymph nodes.
Later, it reaches the blood, which transports it to various organs, where it reproduces again (especially the liver and spleen). From here it returns to the blood, which eventually leads to the skin.
You may be interested in: Eczema of the skin: causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Pathological process
Initially, prodromes are evident (nonspecific symptoms that augur the appearance of the disease). In this case , a flu-like picture occurs. After this, an exanthematic disease occurs (one that occurs with a skin rash).
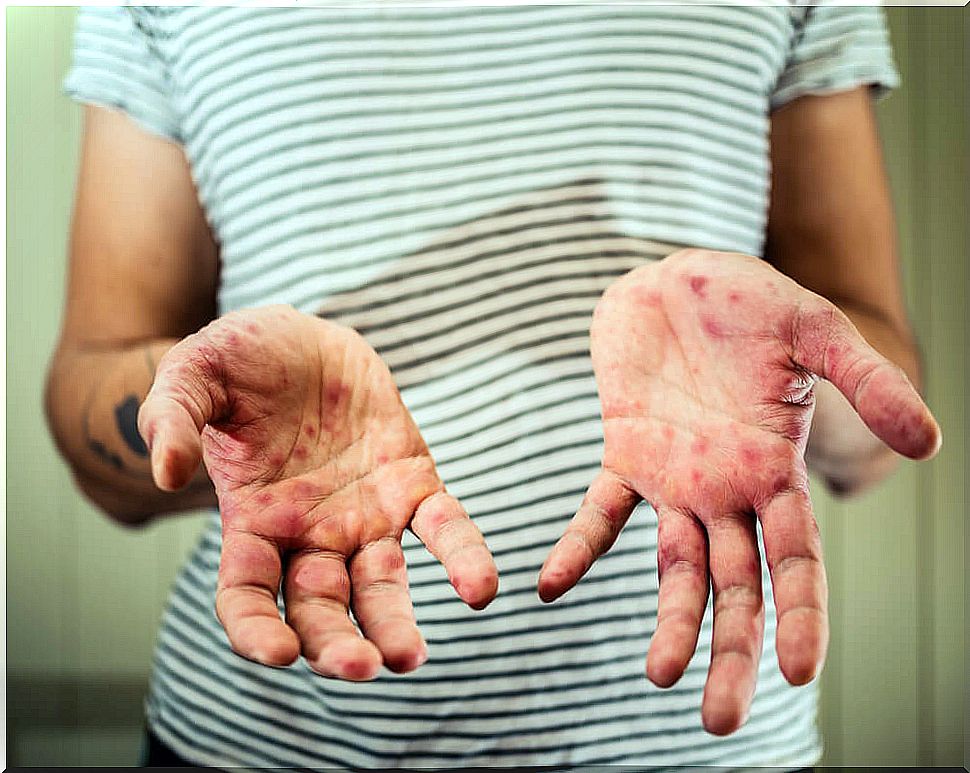

- Macular rash (red but flat rash) appears first, which then becomes papular (raised, with solid content).
- Later vesicles appear, which are also elevated, but whose content is liquid.
- Finally, the scabs appear, which are the expression of the wound healing. Some of these injuries can leave scars.
After illness
VZV belongs to the herpes virus family. Like the viruses in its family, after having caused the disease, it remains quartered, latent (“asleep”) in sensory ganglia. These ganglia correspond to groups of neurons.
VZV is reactivated in approximately 10-20% of cases. It leaves the sensory nodes in the back and causes the disease known as shingles. It is similar to a common herpes but extremely painful and affects a region of the back.
Also visit: How dangerous is chickenpox in adults?
Why you only have chickenpox once
The answer to this question is explained based on the immune response, its phases and characteristics.
Primary immune response
When an infectious agent comes into contact with the body for the first time, the immune system causes two types of cells to reproduce primarily :
- Lymphocytes: produce antibodies, which bind to the infectious agent and neutralize or signal it so that other immune cells know that they have to attack it.
- Macrophages: they directly “eat” the infectious agent.
The primary immune response is slow and not very intense. For this reason, the disease develops but is finally fought and disappears. During this response, memory lymphocytes are also generated, which remember the infectious agent for a variable period of time. In the case of chickenpox, this period of time is (usually) a lifetime.
Secondary immune response
In a second contact of the infectious agent with the organism, the memory lymphocytes act immediately. These generate a much faster, more intense and permanent response. Thus, the disease ends up not developing.
So we could say that in memory lymphocytes is the key that chickenpox is only had once in life.