Everything You Need To Know About Vitamin B12
A deficiency of vitamin B12 can cause anemia in the medium term. This is a common disorder of vegan diets, lacking in this nutrient.

Vitamin B12 is essential for the body as it helps it carry out different important processes, such as converting the food we eat into glucose.
Join us to discover everything you need to know about vitamin B12, also called cobalamin. We will tell you in what functions it intervenes and how, in addition to recommending some foods that provide it. Find out!
All about vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a vital role in red blood cell formation, cell metabolism, nerve function, and DNA production. Also, cobalamin helps prevent megaloblastic anemia.
1. Recommended daily dose
The amount of vitamin B12 you should eat will depend on your age. Thus, babies should ingest between 0.4 and 0.5 micrograms during the first year of life and 0.9 micrograms up to 3 years.
The recommended dose for children is 1.2 micrograms up to 8 years, 1.8 micrograms up to 13 years and 2.4 micrograms up to 18 years. Then the dose remains stable.
Pregnant or lactating women should ingest 2.6 and 2.8 micrograms respectively.
2. How it is absorbed
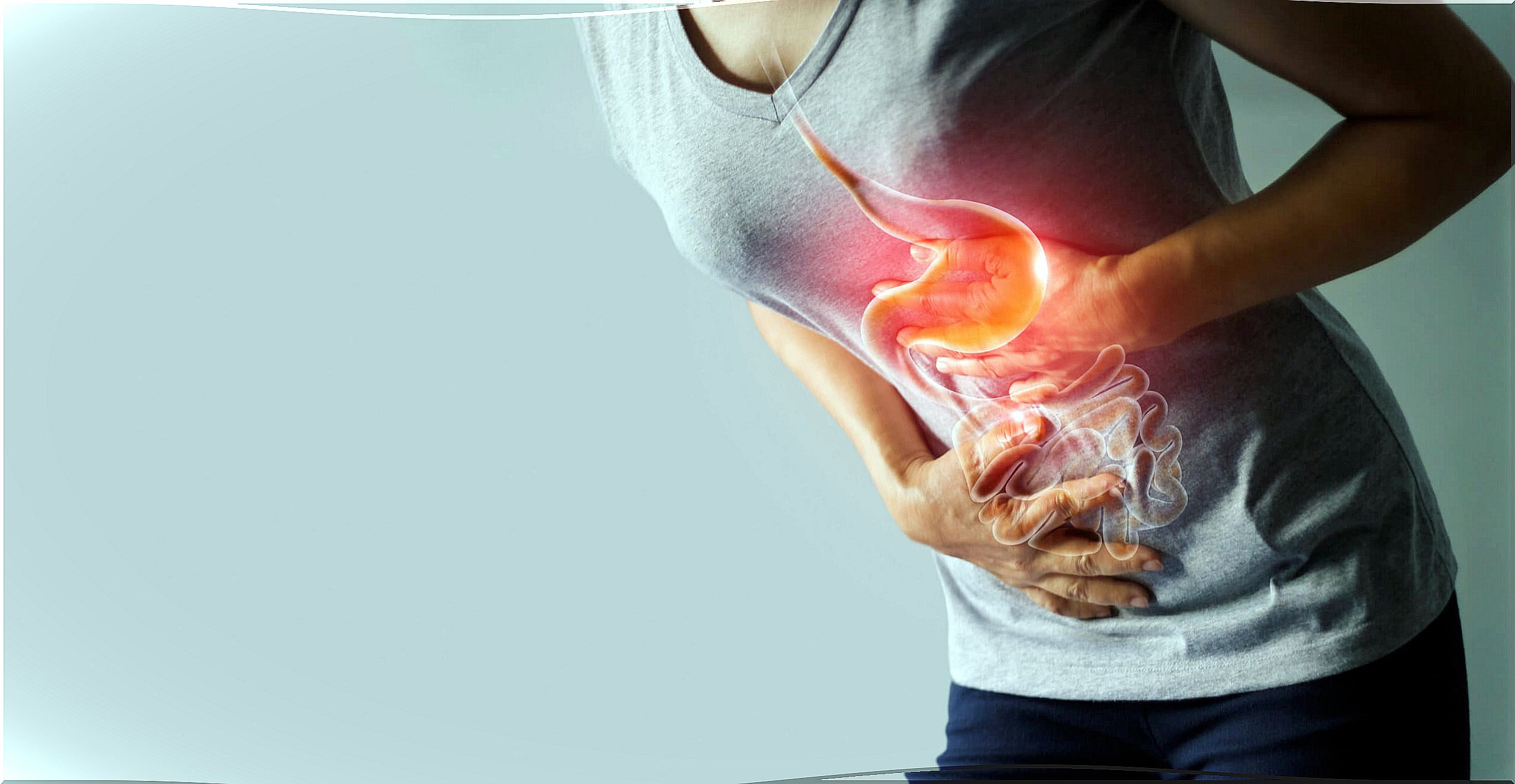
When eating foods rich in vitamin B12, stomach acid separates this vitamin from the protein to which it is attached. Then cobalamin is combined with intrinsic factor (a stomach protein) to achieve absorption.
Those people who for some reason cannot produce intrinsic factor (for example, suffering from pernicious anemia) often have problems absorbing this nutrient.
This is the main cause of vitamin B12 deficiency. If there are no absorption problems, the incidence of its deficiency is usually minimal since the body has the ability to store it in large doses for later use, even within a few years.
Only in the case of people who follow vegan diets, lacking in this nutrient, can pose a risk of deficiency of it, as stated in an article published in the journal “Nutrients”.
Despite being difficult to suffer from a deficiency of this vitamin, it is not impossible. People who suffer from it show symptoms such as:
- Pricking sensation in hands and feet.
- Movement problems, due to peripheral nerve damage.
- Pale or yellowish skin
- Extreme fatigue, related to pernicious anemia.
- Fast heartbeat
- Short of breath.
3. Benefits of cobalamin
At the beginning of this article we mentioned that this vitamin is essential for the development of the body, highlighting its main functions. Let’s now see its most important benefits:
- It can lower the risk of heart disease.
- It will help decrease the risk of birth defects.
- It prevents megaloblastic anemia, by ensuring the correct formation of red blood cells, according to a study published in the journal “American Family Physician”.
- Maintains bone health, preventing osteoporosis. Different studies have found that B12 deficiency is related to low bone density.
- It reduces the risk of macular degeneration, by reducing homocysteine, the high levels of which are associated with this disease.
- Improves mood. Research has found an improvement in people suffering from depression by combining the medication with a vitamin B12 supplement.
- Increase memory.
- It is used for the growth of hair and nails, in addition to promoting skin health. This is due to its work at the level of cell production.
4. Foods rich in vitamin B12
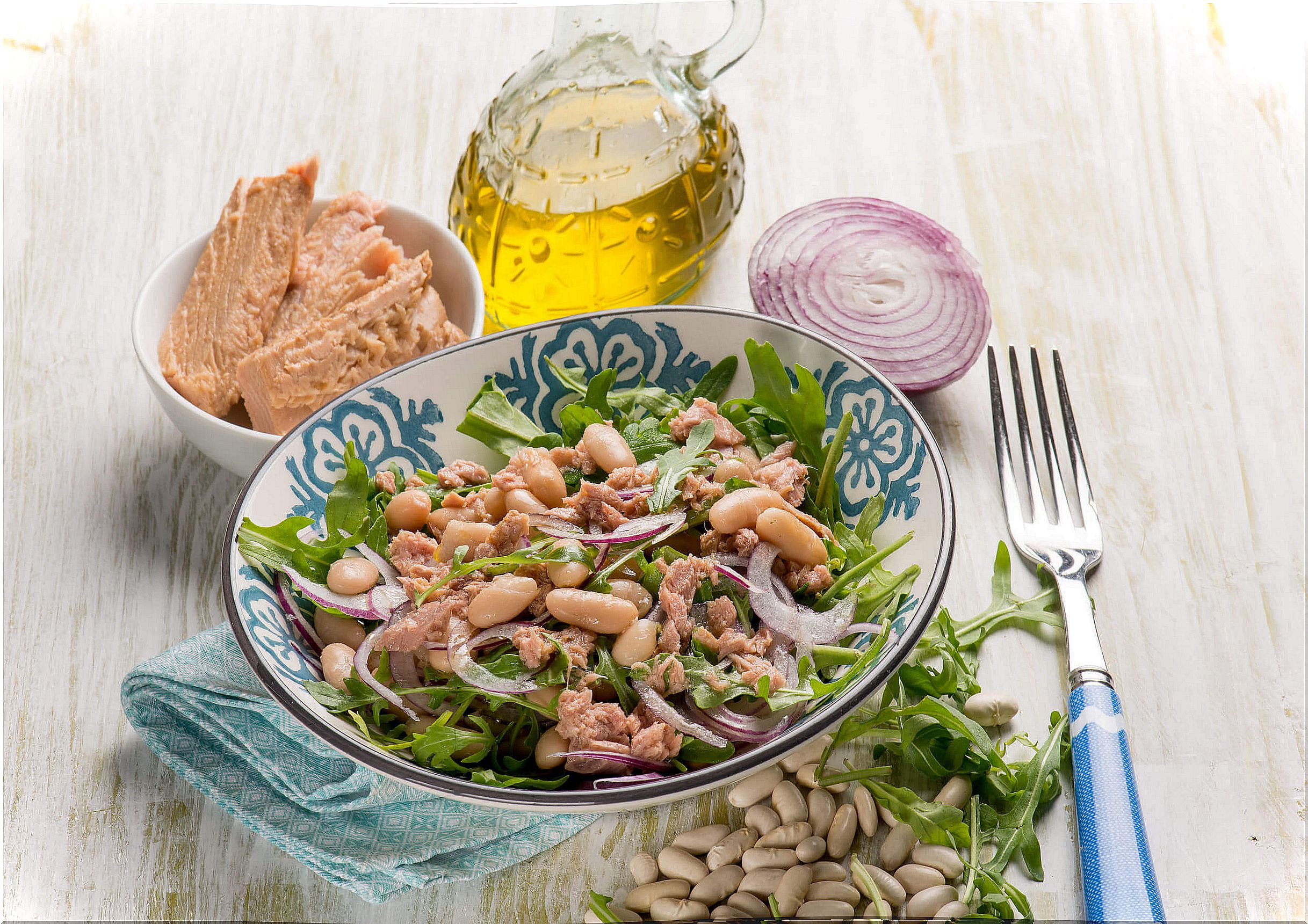

This vitamin is present in different foods, especially those of animal origin. For this reason , people who follow a vegan or vegetarian diet could suffer a deficiency and it is necessary to assess their supplementation. Among the main foods that provide cobalamin we find:
- Liver and kidney: they are the two cuts with the highest amount of vitamin B12, especially those of lamb. Lamb liver provides 990% of the recommended daily dose per 100 grams.
- Clams: not only provide this vitamin but also antioxidants and proteins.
- Sardines: its contribution per 150 grams is twice the recommended dose of vitamin B12.
- Fortified cereal : choose cereals fortified with this vitamin. Check its label before buying!
- Tuna: 100 grams of tuna provide 160% of the necessary dose.
- Salmon: 180 grams of salmon provide 80% of the recommended dose.
Pay attention to your vitamin B12 intake
If you experience any of the symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency mentioned, do not hesitate to see your doctor to evaluate if you have pernicious anemia. Remember that no one better than the specialist can guide you to have a balanced and healthy nutrition.