Dislocation: Causes, Symptoms And Treatment
Dislocations are one of the most painful injuries. The bones that make up a joint generally lose their normal configuration as a result of trauma.
A dislocation is a pathology, usually caused by trauma, in which a joint loses its normal configuration. That is, the bones that make up the joint move as a result of a blow.
Dislocations are an emergency, they require immediate intervention. They mainly affect the joints of the limbs, such as the shoulder or the hip.
Anatomical memory of the joints
The bones that make up the skeleton are rigid and resistant structures. Instead, it is the skeleton that gives us mobility. To allow movement there are the joints, which are the joints between the different bones.
The bones are attached to each other by ligaments. They are elastic structures that are inserted into the bones allowing a certain degree of mobility. In addition, to avoid the friction of one bone against another, which would cause the wear of the tissue, there is cartilage on the articular surfaces. It is known as articular cartilage.
In more mobile joints , called synovial joints , there is a capsule of fibrous tissue that surrounds the joint surfaces (the parts of the bones covered by cartilage).
It is called the synovial capsule and forms a space filled with fluid (synovial fluid) that also helps facilitate movement by reducing the stresses on the bones.
In relation to the joints there are also the tendons. Tendons are the part of the muscle that attaches to the bone. Thus, when a muscle contracts, it pulls the bone to which it is attached and movement occurs. When the muscle relaxes, the bone returns to the starting position. The attachment of the tendon to the bone is known as enthesis.
Why does a dislocation occur?
In dislocations, what happens is that the bones that make up a joint lose their normal configuration. This can injure the capsule, ligaments, and surfaces of the joint. It is what is known as the soft parts of the joint.
Although there are other causes, most dislocations are caused by high-energy trauma. People who have already suffered from such pictures are at greater risk of having a dislocation, since the soft tissues are injured and may not fully recover.
Alterations in the ligaments, muscle weakness or joint malformations can increase the risk of suffering dislocations. The same happens in those patients who have a prosthesis. This is due to the fact that in them there is already a basic articular weakness, which favors that after a trauma the bone can be mobilized.
Clinic of a dislocation
If the consequence of a blow or fall has been a dislocation, the affected joint will be swollen and red. It is not difficult to imagine that the subject will feel a lot of pain and will not be able to move it properly, that is, there will be functional impotence.
These are the common signs of any joint injury after trauma. In addition, the dislocation leads to a great deformity of the joint because the bone has moved from its normal location.
Also, due to the injury, the synovial fluid fills with blood from the damaged tissues. This is known as hemarthrosis, which is also common in hemophiliac patients.
The danger of this injury, in addition to the bone leaving the joint, is that there may be compression of a nerve or blood vessel. These structures are in relation to the joints, running between the muscles of the extremities.
If these structures are compressed, the joint may not receive blood, if it is an artery; or the nerve transmission is interrupted, affecting mobility and sensitivity, if it is a nerve.
In summary, the most common symptoms in a dislocation are the following:
- Pain in the injured area.
- Swelling in the injured area.
- Malformation of the dislocated area.
- Bruising or redness of the injured area.
- Numbness or weakness in the injured area.
- Difficulty using or moving the injured area normally.
Types of dislocations
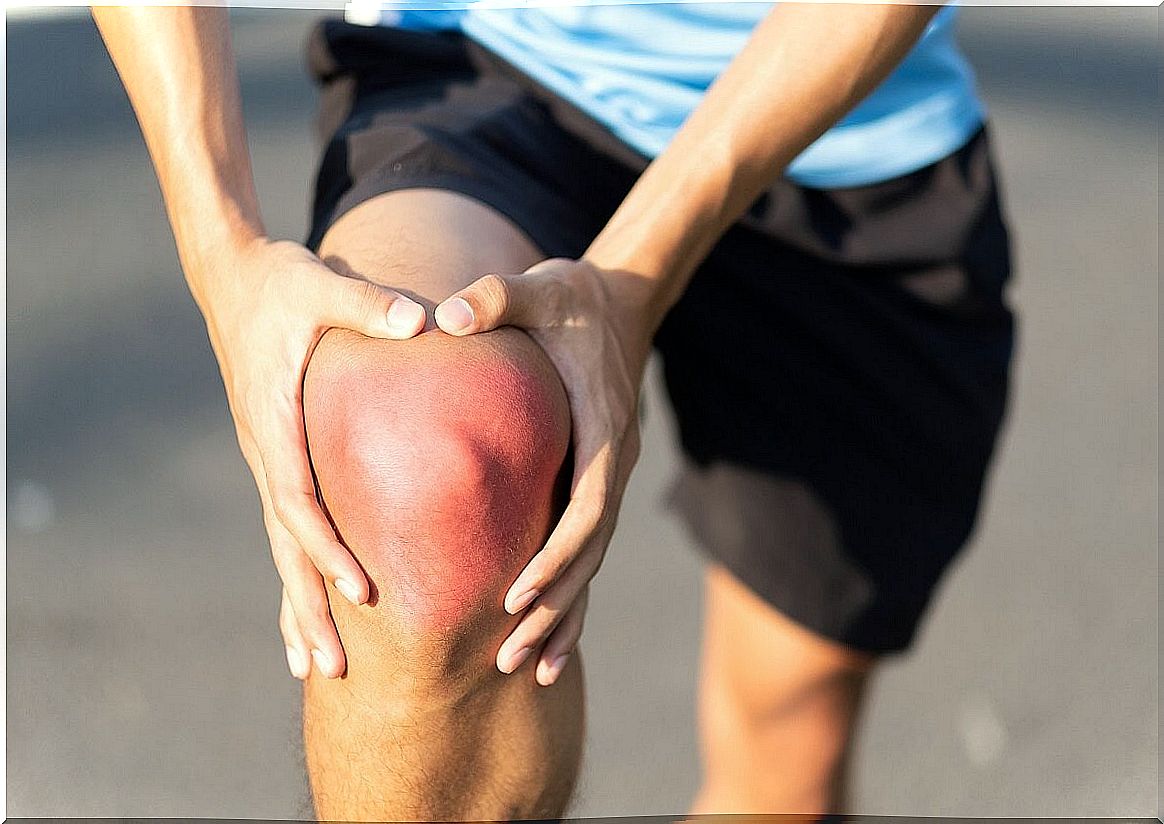
Depending on the evolution and characteristics, there are different types of dislocations:
- Acute: those that occur after a more or less severe trauma. There is no history of other dislocations nor do they have complications.
- Or chronic inveterate: bone lesions are cured in a process called consolidation without scarring. In soft tissue injuries do heal based on fibrous tissue. If the bone is not within the joint, the soft tissue scar occupies this space, making it difficult for the bone to return to its original position.
- Recurrent : are those that occur in a joint that has already suffered a dislocation. The soft tissues can be injured after a first injury, so that the picture can be repeated in similar or even less intense situations. It is common in athletes.
- Common : refers to those suffered by people with a basic joint pathology. There are diseases that affect the ligaments, the joint capsule or other structures. If these tissues are weak, dislocations are more frequent. This is what happens in pathologies such as Marfan syndrome.
Treatment of dislocations
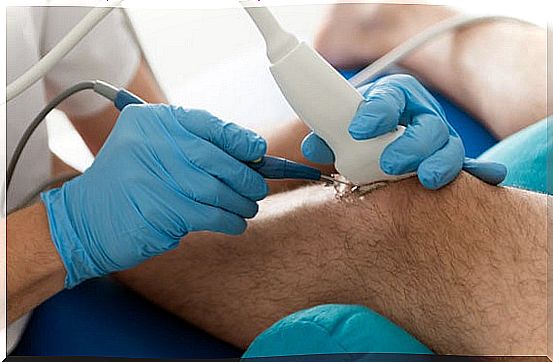
Treatment of a dislocation must be immediate. Initially, rest, ice, compression, and elevation are recommended. Dislocations can reduce on their own spontaneously.
If the dislocation does not reduce itself, the bone must be repositioned in its initial position, it is said that the dislocation must be reduced. It can be done under anesthesia, depending on the time that has passed and the affected joint will be done manually or require surgical intervention.
For example, long- standing and recurrent dislocations are reduced by surgery. The same occurs when there is vascular, nervous or dislocation of the vertebrae.
After reduction, the joint must be immobilized for a variable time. After a few days, you have to start rehabilitation exercises to begin to regain mobility.