Anatomy And Function Of The Hair Follicle
It is important to know how the hair follicle works and what it is made of, since this part is a storehouse of stem cells that are used for new research.
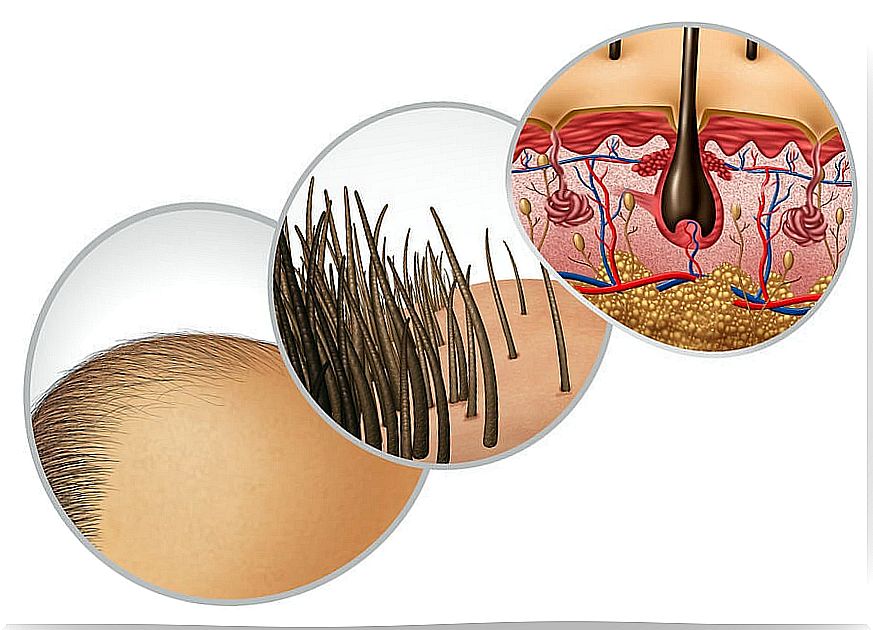
The hair follicle is a cavity in the skin where hair grows. It extends from the superficial layer of the skin, or epidermis, to the deep layer, or dermis. It also penetrates a little into the fatty layer under the skin, which is called the hypodermis.
Hair follicles are all over the skin , except on the lips and the soles of the hands and feet. Therefore, if you want to know what parts they are made of and how they are being used in the field of research, we invite you to continue reading.
Hair follicle anatomy
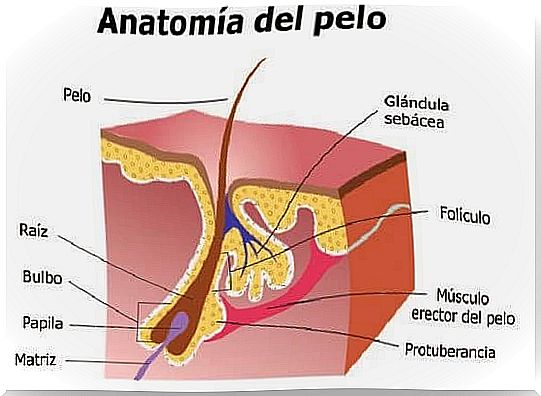
According to an article published in 2019 by the Journal of the Colombian Association of Dermatology and Dermatological Surgery , the hair follicle is composed of several parts, which gives it a complex structure. The basic components of this small gland are :
- Sebaceous glands. They produce sebum, a greasy substance that lubricates the surface of the hair. They are located in the middle dermis and are made up of cells that contain lipids. Therefore, the secretion of these glands is continuous.
- Bulb. It is an expansion of the hair follicle that originates in the deepest part of it. It is the “germination matrix” of the follicle because that is where the cell division that gives rise to the hair occurs. In addition, it is covered by nerve fibers.
- Dermal papilla. It is a small cone-shaped structure. It is made up of fibroblastic cells, which are responsible for hair formation and hair cycles. They supply nutrients to the hair.
- Follicular canal. It is the cavity where the hair grows.
- Erector muscle. It forms in the adjacent dermis and reaches the hair follicle. It is found inserted in the dermal papillae. When it contracts, the hair stands on end. In this case, dimples are formed that are popularly known as “goose bumps”.
- Apocrine sweat glands. Although they are not part of the follicle, they lead to it. They are found in areas where there is a greater amount of hair, such as the scalp, genitals and armpits.
It is interesting to know that the hair follicle is considered one of the most dynamic skin structures in the body.
The hair growth cycle
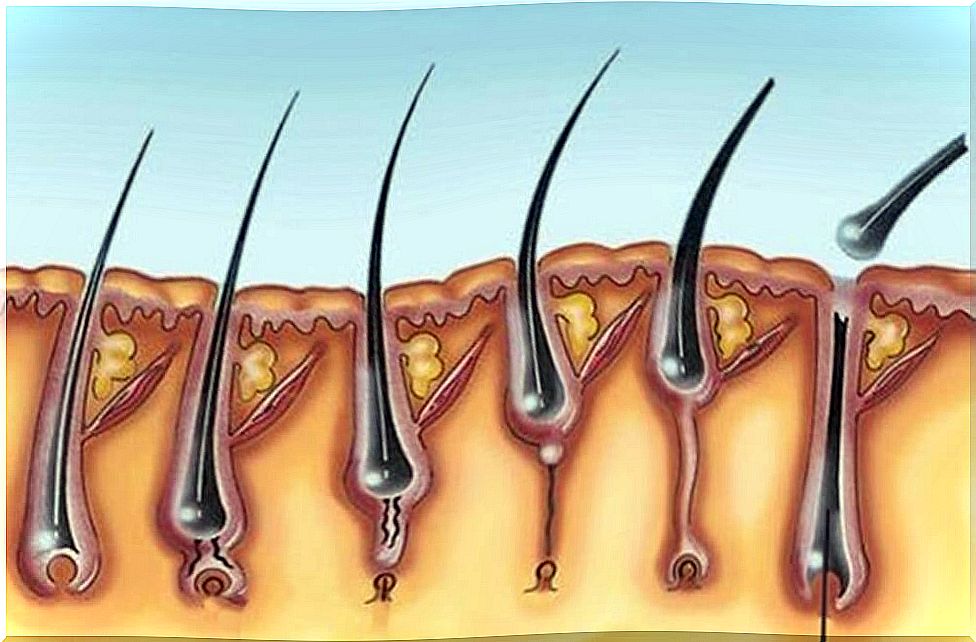
The following article published by the Argentine Journal of Dermatology indicates that the human being has around five million hair follicles. These give rise to two types of hair: terminal hair and downy hair.
The first is longer, thick and pigmented. These hairs extend to the subcutaneous tissue and appear on the eyebrows, scalp, pubis, armpits, etc.
The latter are finer, shorter and are not pigmented. These only reach the superficial and middle dermis. Therefore, they correspond to the fine and colorless hair that covers the body of children and adults. However, there are also indeterminate hairs, which have characteristics of both.
According to an article published by the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology , the hair growth cycle consists of three phases:
- Anagen. It lasts between 2 and 7 years. It is the stage of active hair growth. However, on the eyebrows it only lasts for a few months.
- Catagen. It is a phase of involution that lasts between two and three weeks.
- Telogen. It lasts around 100 days and is a resting phase. The hairs that are in this stage are dead; They are called “club hairs” and about 100 of them are shed from the body each day.
However, as the following study carried out by the dermatologist Aurora Guerra Tapia shows , not all follicles are in the same phase at the same time. In fact, about 90% are in the anagen phase, 10-14% are in the telogen phase, and only 1-2% are in the catagen phase.
Hair follicles and stem cells
The hair follicle contains several types of cells and among them stem cells stand out. In fact, the follicle is the most abundant part of stem cells in the skin.
These are located in a prominence called the “bulge” that is at the insertion point of the erector muscle. Due to this location, access to stem cells is easier than in other parts of the body.
Advances in understanding the structure of the follicle are making possible the medical use of stem cells in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
The possibilities this offers are vast. For this reason, research is being carried out today to generate human hair follicles with good prospects.
If achieved, it would be a revolution, because as the following article published by the Journal of Pineal Research well describes, it could be applied to the broad field of alopecia (hair loss).