Atelectasis: What Is It And Why Does It Occur
Atelectasis is a lung disorder in which part of the lungs collapses as a result of loss of alveolar volume.
It is generally of idiopathic cause, that is, it is not known or there are so many that it cannot be determined what it is. Chest trauma, pneumonia, hormonal problems or respiratory failure derived from other pathologies can cause atelectasis, according to health experts.
Physiological bases of respiratory function
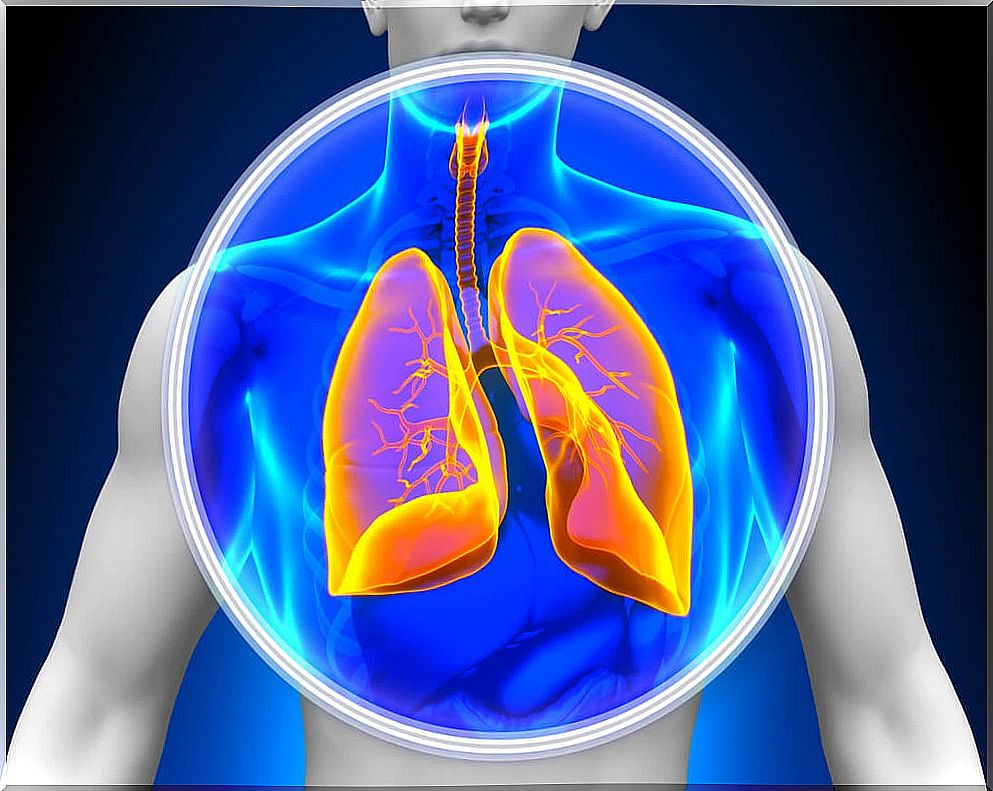
First, the main function of the lungs is to provide oxygen to the blood and remove excess carbon dioxide produced in cellular respiration. This is accomplished by inhaling oxygen-rich air and exhaling carbon dioxide-rich air.
This air reaches the alveoli , tiny grape-shaped structures covered by a large number of tiny blood capillaries. In them gas exchange takes place.
In order for the alveoli to perform their function, they must always remain open and filled with air. This process is complicated during exhalation, when the alveoli have a natural tendency to close and collapse.
How to avoid collapse?
The key is in the substance that covers them, which acts in a similar way to how the oil that is used to grease the hinges of a door does.
- The substance produced by type II pneumocytes that covers the surface of the pulmonary alveoli is known as pulmonary surfactant .
- Surfactants, also known as surfactants , are molecules that lower surface tension. And what is surface tension? The amount of energy required in a liquid to increase its surface area per unit area.
A simile: the typical children’s toy with which they create soap bubbles. In this case, the soap would function as a surfactant, reducing the surface tension of the bubbles. The lower the surface tension, the larger the size of the bubbles.
If we tried to create bubbles only with water we would be incapable because its surface tension is very high. In fact, it is so large that some insects take advantage of it to walk on water, such as the shoemaker.
Similarly, if the pulmonary alveoli were not coated with surfactant, they would close and would not be able to perform their function. When there is a deficiency of surfactant, some trauma occurs, or breathing is made difficult by excess secretions, there is a risk of atelectasis.
However, the human body itself has mechanisms to reduce the probability of this happening. Periodic deep breaths taken unconsciously or coughing to clear excess secretions from the airways are two of these mechanisms.
Causes of atelectasis
The character of this pathology is usually idiopathic. For example, a disorder in the endocrine system in which hormone levels are altered. A decrease in the levels of hormones that promote the synthesis of surfactant by pneumocytes, such as prolactin or thyroxine, can lead to atelectasis.
On the other hand, collapse can be triggered by the obstruction of one of the parts in which the lungs branch: the bronchi. This obstruction can be due to inhalation of a foreign body, such as a piece of food or a toy, the presence of a mucous plug, or even a tumor.
Alternatively, the obstruction can be caused by something compressing the bronchus from the outside. It can be trauma, swelling of a nearby lymph node, or, again, a tumor.
In addition, other pathologies associated with the lungs can lead to bronchial blockages. This is the case of an increase in the fluid contained in the pleural space, a condition known as pleural effusion. Or also from the entry of air into this same space, which is known as a pneumothorax.
Diagnosis and treatment
According to the MSD Manual, “Doctors suspect atelectasis based on the person’s symptoms, physical examination, and the context in which the symptoms occur.” However, the diagnosis is confirmed by a chest X-ray. This is the test that allows us to observe if any bronchus is obstructed or if the alveolar volume is unusual, and if there are any complications.
On the other hand, the treatment of this pathology usually consists of resolving the obstruction of the airways and ensuring a deep breath. Depending on the case, bronchoscopy or other methods will be evaluated, such as surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or laser therapy.








