8 Foods That Provide Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a nutrient with very important functions in the body. Although much of it is obtained by exposure to the sun, it is also possible to supplement its absorption through diet.
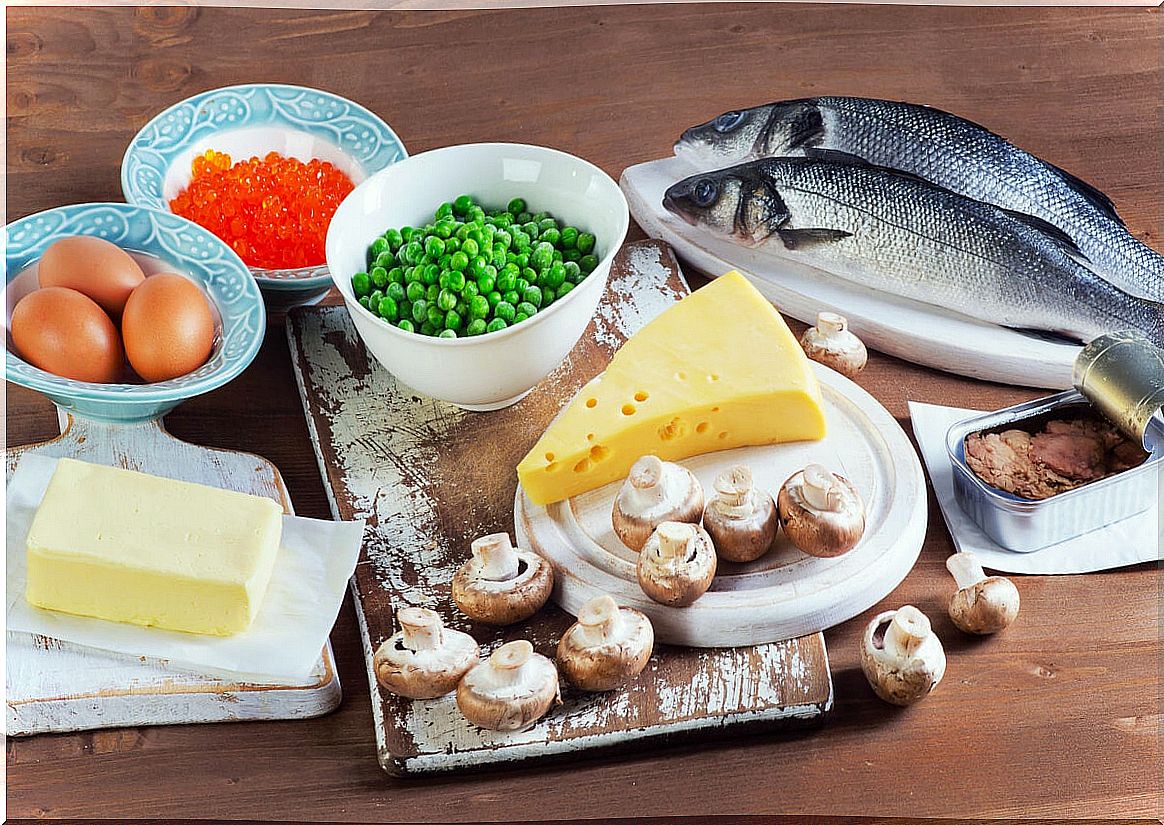

Foods with an abundant content of vitamin D are essential in the diet. Although much of this nutrient is produced by exposure to sunlight, some animal and plant products also provide it in significant amounts.
As an article published in the Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics explains , optimal doses of vitamin D are essential for health. However, it is estimated that 50% of the world population has a deficit of it. How to get it? Below we detail options that you can incorporate into your diet.
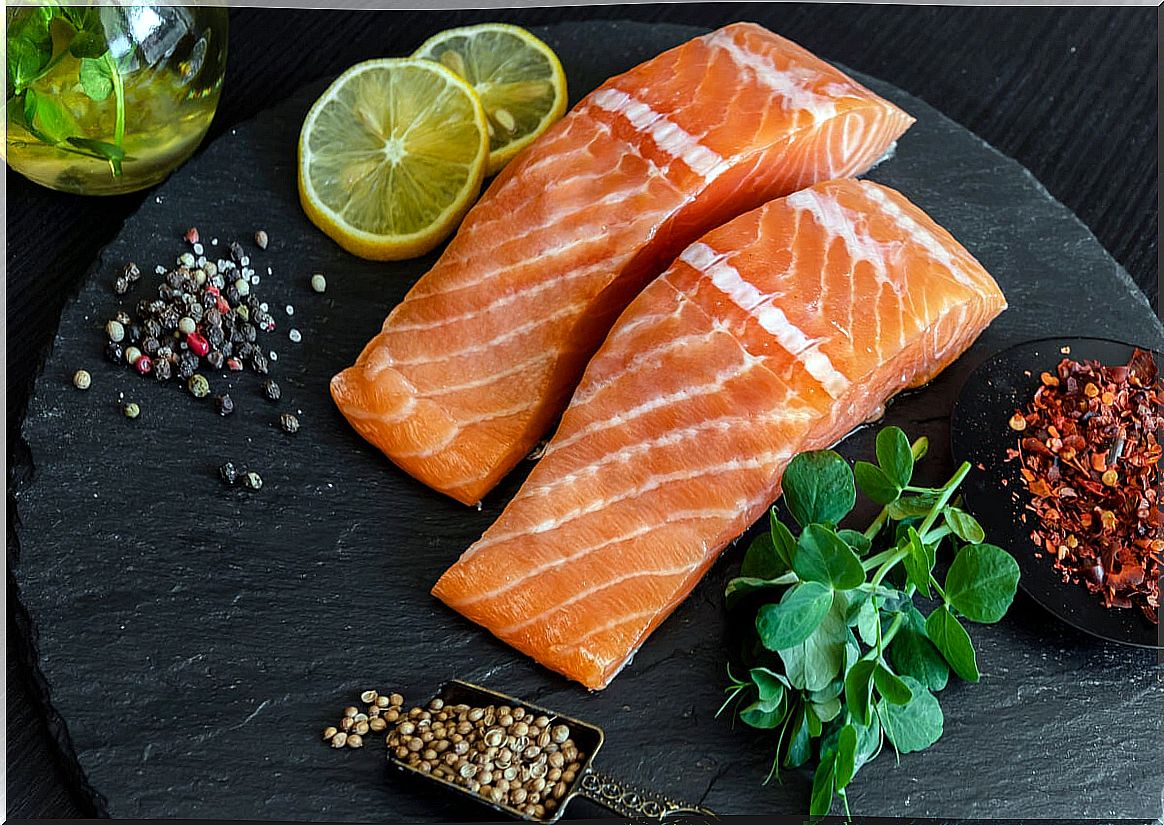
1. Salmon
Salmon is one of the most prominent foods for its nutritional properties. In addition to providing an interesting dose of omega 3 fatty acids, it also contains vitamin D.
According to information from the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) food composition database , each 100-gram serving provides 526 IU (international units) of vitamin D, which is equivalent to 66% of the values recommended daily.
Even varieties such as wild salmon make a greater contribution. In the data compiled by a study in The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology it is stated that this type of salmon contains up to 1,300 IU per serving.

2. Crimini mushrooms
The crimini mushroom (Agaricus brunnescens) is also known as “Italian brown mushroom.” It has a similar appearance to the white mushroom, but its hat is brown. According to the SELF Nutrition Data database, they provide 31.9 micrograms of vitamin D per 100 grams. That is, it reaches up to 160% of the recommended daily values (DRV).
3. Herring
Herring is another variety of fish that makes important nutritional contributions. In particular, it is a source of protein, vitamins, minerals and essential fatty acids. It is typically served raw, canned, smoked, or pickled.
It is estimated that every 100 grams contains up to 216 IU of vitamin D, that is, 27% of the recommended daily values. However, when it is prepared in recipes such as marinade, this amount is reduced to 112 IU per serving (14% RDV).
4. Canned sardines
Sardines have become popular as an ideal food to improve the quality of the diet. There is even research that associates its consumption with better metabolic health. As if that were not enough, it also stands out as one of the most abundant foods in vitamin D.
Specifically, 100-gram servings contain up to 177 IU of vitamin D, or 22% of the daily values. Added to this, it also provides healthy fats, protein, and minerals.
5. Egg yolks
The egg is a food known for its versatility and for its properties. Although much of its protein content is in the white, the yolk contains essential fat, vitamins and minerals. Information compiled in the medical journal Advances in Nutrition states that a yolk contains 37 IU of vitamin D (5% of the required daily value).
6. Fortified tofu
Tofu is one of the most popular soy products. Usually it is distributed with formulas enriched with vitamin D in its composition. To be more precise, 100 gram servings contain up to 13% of the recommended daily values for this nutrient.
7. Fortified cereals
Fortified cereals are also foods that provide vitamin D. Although their content is lower compared to the other sources mentioned, regular consumption is still a good option to obtain this vitamin.
As detailed in the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Food Composition Database, these foods provide between 54 and 136 IU of vitamin D (17% of the VDRs).
8. Fortified yogurt
Due to the needs of vitamin D, both yogurt and other dairy products have been fortified with this nutrient. However, not all market presentations have this feature. That is why it is important to read the labels before purchasing the product. Often, it contributes 7% of the daily requirement of vitamin D.

What is the function of vitamin D in the body?
Vitamin D is a type of fat-soluble vitamin whose assimilation plays a very important role in health. Like other fat-soluble substances, such as A, E and K, it is absorbed with fat and stored both in the liver and in other lipid tissues.
According to a publication in the National Center for Biotechnology Information , there are two main forms of this nutrient in the diet: vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) and vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol). The latter, in addition to being present in foods of animal origin, is also obtained by exposure to the sun.
Among other things, it should be noted that D3 is twice as effective in raising overall blood levels. This, in turn, is associated with a number of health benefits. To be more precise, this nutrient has the following functions:
- Control blood levels of calcium and phosphorus.
- Strengthen the immune system and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Reduce the risk of fractures and bone diseases.
- Take care of heart health.
- Reduce the risk of premature aging.
What is the relationship between vitamin D and the sun?
Not surprisingly, vitamin D is also called the “sunshine vitamin.” Although the aforementioned foods contain this nutrient, much of the production occurs when the skin is directly exposed to the sun. Even most people meet at least part of their needs in this way.
Also, the vitamin D that is produced in the skin can last up to twice as long in the blood compared to that obtained from the diet. For this reason, as an article in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition explains , it is advisable to sunbathe in moderation.
What are the recommended levels of vitamin D?
Recommended levels of vitamin D can vary based on age and gender. Likewise, it is possible that they change during pregnancy or when suffering from certain diseases. To be more precise, Medline from the US National Library suggests the following:
Infants
- 0 to 6 months: 400 IU (10 micrograms -µg- per day).
- 7 to 12 months: 400 IU (10 µg / day).
Kids
- 1 to 3 years: 600 IU (15 µg / day).
- 4 to 8 years: 600 IU (15 µg / day).
Older children and adults
- 9 to 70 years: 600 IU (15 µg / day).
Adults over 70 years
- 800 IU (20 µg / day).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- 600 IU (15 µg / day).
In the case of diseases such as osteoporosis, cancer or cardiovascular diseases, the amounts of vitamin D must be adjusted. If so, it is best to follow the doctor’s recommendations. Similarly, it is necessary to avoid exceeding the suggested dose.

Foods with vitamin D as part of a healthy diet
Foods that contain vitamin D are ideal to obtain it with the diet. However, they must be included in the framework of a healthy and varied diet that provides all the nutrients that the body requires.
Also, remember that much of your vitamin D is obtained through exposure to the sun. That is why it is convenient to take sunlight in a moderate way, either in the morning until 11:00 or in the afternoon after 16:00.